Spring-入门 [toc]
0、参考资料 书:
博客:
视频:
【根据视频总结笔记】:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45496190/article/details/107059038 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45496190/article/details/107067200 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45496190/article/details/107071204 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45496190/article/details/107082732 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45496190/article/details/107092107
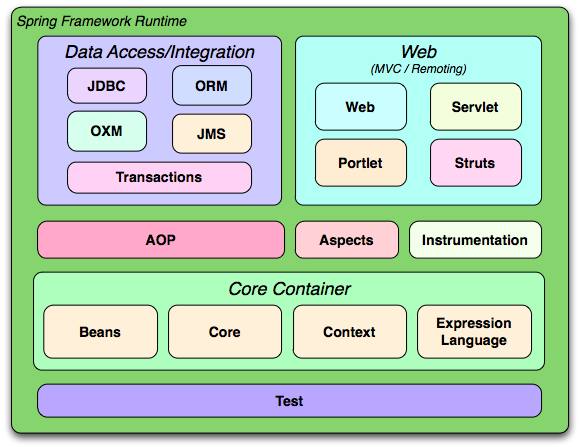
1、Spring基础 1.1、Spring 概述 1.1.1、什么是 Spring Spring 是一种JavaEE 开发一站式的解决方案。以 IOC 和AOP为核心,该框架提供的功能贯穿表示层、业务层、持久层 。
Spring框架的特点:
轻量 :核心Jar包只有1.4 MB,占用的系统资源(CPU和内存)少。
框架灵活 :可以按需引入模块来实现不同的功能。
面向容器 :(以XML或注解的形式)配置化实现对象,管理对象的生命周期。
控制反转(IOC) :创建对象时,若需要依赖其他对象,则自动传入其依赖的对象。(目的:解耦)
面向切面(AOP) :将 业务逻辑 和 系统逻辑 分离,提高系统的内聚。
Spring的组成架构:
spring 框架的核心模块包括:
核心容器层:beans、core、context、spEl(核心容器的运行还需要commons-logging包)
数据访问层
Web应用层
Jar包介绍:
主要为三类:
class字节码文件的压缩包
API文档的压缩包
源码压缩包
1.1.2、 IoC 与 DI IoC(Intervision of Control)也叫 控制反转 。
DI(dependency Inject)也叫 依赖注入 。
IoC是由Spring的 IoC容器来管理Java对象的生命周期,把控制权交给IoC容器,直接从IoC容器中获取对象,而不需要像传统的面向对象编程那样由用户手动new出对象。IoC理论实际上是在借助第三方的 IoC容器实现多个对象之间的解耦。【相当于:先整体,再局部】
DI是在IoC容器创建对象的过程中,若A对象依赖B对象,则由 IoC容器主动创建B对象并传给(注入)A对象。
IoC 和DI是从不同的角度对同一件事情的描述。IoC是从容器的角度,DI 是从APP的角度。
使用 IoC/DI 的好处:
可维护性好
专注业务
可复用性好
创建对象具有热拔插性
1.2、Spring 的核心容器 由上面1.1.1小节的Spring组成架构图可以看出,Spring的核心容器的模块分为:
beans:工厂模式,管理对象
core:IoC、AOP
context:在beans和core的基础上构建,继承了beans模块,添加了国际化、事件传播等功能
spEL:Spring表达式(类似El表达式的写法)
Spring框架的核心容器中,主要的两个包为:org.springframework.beans.factory和org.springframework.context。其中,beans 包 中主要的接口为BeanFactory,负责管理Java类;context 包 中主要的接口为ApplicationFactory。
本质上IoC容器就是一个工厂。使用了XML解析、工厂模式、反射。
Spring 中 的 IoC容器的组成部分主要有:
对象
配置文件applicationContext.xml:bean的id、类、属性、属性值。xml配置文件名可以随意。
BeanFactory 接口及相关组件:工厂模式(Bean容器模式),负责读取配置文件、管理对象的生成和加载。维护Bean对象之间的依赖关系,负责Bean的生命周期。加载配置文件时,不会创建对象,使用对象时,才创建对象【Spring使用】
ApplicationContext 接口及其相关类:相比BeanFactory接口来说,该方式可以更方便的访问资源、支持国际化消息、提供文字消息解释方法等。加载配置文件时,创建对象【程序员使用】
BeanFactory 接口的实现类:
org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory:需要传入一个Bean配置文件文件(applicationContext.xml)的输入流,然后调用getBean(String id) 或getBean(String id,Class requiredType)来创建相应的对象。
ApplicationContext 接口的实现类
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:从文件系统 中的XML配置文件加载(以盘符为根目录),只能在指定路径中查询配置文件
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从类路径 中的XML配置文件加载(以src为根目录),可以在整个类路径中查询配置文件
XmlWebApplicationContext:从Web系统 中的XML配置文件加载
2、IoC 控制反转 2.1、 Bean的装配-概述 IoC/DI的实现方式(Bean的装配):
两种方式【XML和注解】
类的setter方法(常用):xml中bean节点的property子标签,必须要有无参构造和setter方法
类的构造方法:xml中bean节点的constructor-arg子标签
注解装配(必须导入AOP的jar包)):@Repository(dao层)、@Service、@Controller、@Autowired
xml中bean标签的自动装配属性
注意 :
@Component注解可以泛指@Repository、@Service、@Controller
以下四个注解用于创建对象:@Component、@Repository、@Service、@Controller 。
IoC/DI的实现方式(Bean的装配)-简写-命名空间:
p:相当于property标签
c:相当于constructor-arg标签
命名空间的方式与子标签的方式的区别:
命名空间的方式需要引入xml的命名空间
命名空间的方式是作为bean标签的属性来写的,子标签是作为bean标签的内部节点写的
Bean标签的常用属性和子标签:
bean标签常用的属性:
bean标签常用的子标签:
property标签
constructor-arg标签
property标签 和 constructor-arg标签 的常用属性:
name:标识,必须与Java类中的成员变量的名字一致
value:注入java自带的数据类型的数据
ref:注入用户定义的JavaBean的全类名 或bean标签的id
bean的子标签property的常用子标签【集合数据类型】:
list : 配合value标签使用
set
map:配合entry子标签使用(entry标签的属性:key 和 value-ref)
props:配合prop子标签使用(key属性;值放标签内)
null
value
property标签的value为特殊值时:
2.2、 Bean的XML装配 Bean的装配-XML的方式(调用setter方法装配):
引入Spring 的 beans约束
在配置文件中写bean标签
利用ApplicationContext对象的getBean方法获取对象
调用bean对象的方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd " > <bean id ="dao" name ="userdao;UserDao" class ="com.ssm.ioc.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl" scope ="singleton" /> <bean id ="service" class ="com.ssm.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" > <property name ="id" value ="1" /> <property name ="dao" ref ="dao" /> </bean > </beans >
Bean的装配-XML的方式(调用构造方法装配):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd " > <bean id ="dao" class ="com.ssm.ioc.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl" /> <bean id ="service" class ="com.ssm.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" > <constructor-arg index ="0" value ="1" /> <constructor-arg name ="dao" ref ="dao" /> </bean > </beans >
2.3、 Bean的注解装配 Bean的自动装配-注解的方式:
使用注解的形式装配,必须结合AOP的 jar包来完成
XML配置文件中导入名称空间和约束
配置文件的beans标签中:<context:annotation-config/>
配置bean标签(省略property和constructor-arg子标签)或者 开启组件扫描
在Java类上使用注解
创建ApplicationContext对象并获取Bean对象
调用Bean对象的方法
Bean的装配-注解方式注意事项:
自动装配-需要引入的约束:
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
导入某个包的所有Bean
<context: component-scan base-package="包名"/>
自动装配-开启自动装配设置:
<context:annotation-config/>
自动装配-Java类上设置注解:
标识分层:@Repository(beanId)、@Service(beanId)、@Controller(beanId)、@Component【注解的参数可省略,省略后默认为首字母小写的类名 】
标识自动装配:@Autowired 与 @Qualifier、@Resource(name="beanId")
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd " > <context:annotation-config /> <bean id ="dao" class ="com.ssm.ioc.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl" /> <bean id ="service" class ="com.ssm.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" /> </beans >
Service层:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 package com.ssm.ioc.service.impl;import javax.annotation.Resource;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import com.ssm.ioc.dao.UserDao;import com.ssm.ioc.service.UserService;@Service("service") public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService private int id; @Autowired private UserDao dao; @Override public void login () dao.login(); System.out.println("userService: ...login" ); } public UserServiceImpl () super (); } public UserServiceImpl (int id,UserDao dao) super (); this .id = id; this .dao = dao; } public UserDao getDao () return dao; } public void setDao (UserDao dao) this .dao = dao; } public int getId () return id; } public void setId (int id) this .id = id; } @Override public String toString () return "UserServiceImpl [id=" + id + ", dao=" + dao + "]" ; } }
Bean的自动装配-XML的方式:
(利用bean标签的autowire属性,必须导入aop的jar包)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd " > <bean id ="dao" class ="com.ssm.ioc.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl" /> <bean id ="service" class ="com.ssm.ioc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" autowire ="byName" /> </beans >
2.4、 Bean-命名空间装配 Bean的装配-p命名空间(调用setter方法装配):
引入命名空间: xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
编写bean配置文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd" > <bean id ="userDao" class ="com.ssm.ioc.dao.UserDaoImpl" /> <bean id ="userService" class ="com.ssm.ioc.service.UserServiceImpl" p:idx ="1" p:dao-ref ="userDao" /> </beans >
Bean的装配-c命名空间(调用构造方法装配):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:c ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" > <bean id ="thingOne" class ="x.y.ThingTwo" /> <bean id ="thingOne" class ="x.y.ThingOne" > <constructor-arg ref ="thingTwo" /> <constructor-arg value ="[emailprotected]" /> </bean > <bean id ="thingOne" class ="x.y.ThingOne" c:thingTwo-ref ="thingTwo" c:email ="[emailprotected]" /> </beans >
2.5、纯注解装配 不使用XML配置文件【SpringBoot 常使用纯注解方式】
步骤:
编写一个“配置类”,使用@Configuration修饰
“配置类”上使用@Component-Scan(base-Packages="包路径")修饰
创建AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(配置类的字节码)对象来代替ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
2.6、 引入其他配置文件 在beans标签内:
1 <import resource ="applicationContext-123.xml" />
2.7、 Bean的生命周期
调用无参构造
setter方法
初始化方法
使用
销毁方法
3、AOP 面向切面编程 3.1、 什么是AOP AOP也叫 面向切面编程,是对OOP(面向对象编程)的补充。AOP是为了解决实现某个功能时,相同的代码分散到各个方法中【隔离业务逻辑,解耦,提高内聚性】,采用横向抽取机制,利用动态代理技术。
简而言之,AOP就是用不修改源码的方式在主干功能中增加新功能。
3.2、AOP的底层原理 AOP的底层原理【使用的动态代理技术】有以下两种使用情况:
创建代理对象,由代理对象实现功能:
有接口:JDK的动态代理 ,创建接口实现类的代理对象,由代理对象来增强方法。【调用java.lang.reflect.Proxy类的newProxyInstance(接口类加载器,接口的字节码数组,实现InvocationHandler接口来编写增强方法)】
无接口:CGlib的动态代理 ,创建当前类的子类的代理对象,由子类代理对象来完成代理。
3.2.1、 JDK动态代理 JDK动态代理,适用于有接口的情况。
步骤:
创建接口
创建接口的实现类,实现接口的方法
创建InvocationHandler接口的实现类
Proxy.newProxyInstance(接口的类加载器,接口的字节码数组,InvocationHandler实现类的对象);得到对象
对象调用方法
3.3、 AOP术语
Aspect:切面【把通知 应用到切点 的过程 (代码应用到方法)】,切面类需要在beans标签内注册。
Joinpoint:连接点,【一个可以 被动态代理技术增加功能的方法】。
Pointcut:切点,类名、方法名、满足条件的规则【实际 被增加功能的方法】。
Advice:通知(增强),切面类的方法【功能中被增加的代码 】。
前置通知:在被增强的方法运行之前的时候执行
后置通知:在被增强的方法运行之后的时候执行
环绕通知:在被增强的方法运行前后都执行
异常通知:在被增强的方法运行出现异常时执行
最终通知:最终一定会执行的代码
TargetObject:目标对象(增强对象),所有被通知的对象。【被插入代码的对象】
Proxy:代理,通知应用到对象后,被动态创建出的对象。
Weaving:织入,切面代码插入到目标对象后,生成的代理对象的过程 。
术语小结:
切面:一个用于增强其他的类中的方法 的类。
连接点:可以被增强的方法(虚拟的概念)
切点:被增强的方法(实际)
通知:切面类中,用于增强切点的方法的一部分代码
织入:插入通知的过程
AOP常用的两个框架:
Spring AOP:纯Java实现,不需要额外的编译器
AspcetJ:一个单独的AOP框架,需要有专门的编译器【推荐】
AspectJ的切点表达式:
切点表达式的 作用 :表明是对哪个类中的哪个方法进行增强(添加功能)。
语法: execution( [访问修饰符] [返回类型:修饰符为*时省略] [包名.类名] [方法(参数列表)] )
语法示例:
对 com.dao.UserDao的add()进行增强:execution(* com.dao.UserDao.add(..))
对 com.dao.UserDao的所有进行增强:execution(* com.dao.UserDao.*(..))
对 com.dao包内的全部类和方法进行增强:execution(* com.dao.*.*(..))
注意:
上面的表达式 的语法示例中*代表全部,..代表全部
表达式中使用*,则可以省略返回值类型,否则必须写返回值类型
3.4、AspectJ 框架实现AOP AspectJ 框架实现AOP的两种方式:
3.4.1、 XML声明AOP XML声明的有:切面(代理类)、切入点(被增强的方法)、通知(“增强方法”)
XML声明AOP时,所有的 切面(类)、切点(方法)、通知(增加的代码)都必须定义在<aop:config>标签内,beans标签可以有多个<aop:config>标签,每个<aop:config>标签内可以有多个切面(<aop:aspect>)、切点(<aop:pointcut>)、通知(<aop:advisor>)
注解声明AOP-步骤:
定义一个被增强的类,类里定义被增强的方法。
定义一个增强类(切面类,代理类),类中定义不同的方法来代表不同的增强类型。
配置文件中,配置切点
IoC注册bean
AOP配置:<aop-config></aop-config>
配置-切入点:在aop-config标签内,输入<aop:pointcut id="" expression="" />
配置-切面:<aop:aspect ref=""></aop:aspect>
配置-通知:<aop:aspect ref=""></aop:aspect>内,<aop:before method="" pointcut-ref="">
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 // spring的配置文件 <bean id ="userDao" class ="com.dao.UserDaoImpl" /> <bean id ="userProxy" class ="com.demo.UserProxy" /> // AOP配置 <aop-config > // 切点【要被增强的方法】 <aop:pointcut id ="p1" expression ="execution(* com.dao.UserDao.buy(..))" /> // 切面类【代理类】 <aop:aspect ref ="userProxy" > // beforeTest1为切面类UserProxy的【前置通知】增强方法, // 相当于被@Before注解修饰的方法 <aop:before method ="beforeTest1" pointcut-ref ="p1" > </aop:aspect > </aop-config >
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd " > // 注册bean,用于创建对象 <bean id ="userDao" class ="com.dao.UserDaoImpl" > </bean > <bean id ="myAspect" class ="com.aspect.AspectClass" > </bean > // 配置AOP <aop:config > // 注册:切面类 <aop:aspect id ="aspcet" ref ="myAspect" > // 注册:切点 <aop:pointcut expression ="execution(* com.dao.UserDaoImpl.login())" id ="myPointcut" /> // 注册:通知 <aop:before method ="before" pointcut-ref ="myPointcut" > </aop:before > </aop:aspect > </aop:config > </beans >
3.4.2、 注解声明AOP 注解声明AOP-步骤:
定义一个被增强的类,类里定义被增强的方法。
定义一个增强类(切面类),类中定义不同的方法来代表不同的增强类型。
通过配置文件来进行通知的配置,步骤:
开启注解扫描【批量注册类】:<context: component-scan base-package="包名"/>
注解修饰以上两个类【IoC的@Repository、@Service、@Controller】
@Aspect注解修饰(增强类)切面类
配置文件中,开启生成代理对象 的配置:<spo:aspectj-autoproxy/>
配置不同类型的通知【前置、后置、环绕、异常、最终】,步骤:
在增强类 中,在作为通知的方法 上使用不同通知类型的注解 修饰,结合切入点表达式。
注解修饰不同类型的通知-注解类型:
前置通知:@Before(“切点表达式”)
后置通知:@AfterReturning(“切点表达式”)
环绕通知:@Around(“切点表达式”):在通知方法内传入参数,通过在proceedingJoinPoint.proceed()前、后编写代码来实现。
异常通知:@AfterThrowing(“切点表达式”)
最终通知:@After(“切点表达式”)
通知复用【切面类中】:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Pointcut("execution(public void com.dao.UserDao.add(..))") public void pointDemo () System.out.print("通知。。。" ); } @Before("pointDemo()") public void before () System.out.print("前置通知。。。" ); }
多个切面类对同一个类增强时,定义优先级:
使用:@Order(数字)注解修饰被增强的类 ,数字越小,优先级越大
以下示例省略的实体类与dao类和接口的代码:
示例(1)-切面类(增强):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 package com.aspect;import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component @Aspect public class AspectClass @Pointcut("execution(* com.dao.UserDaoImpl.login(..))") public void mypointcut () @Before("mypointcut()") public void before (JoinPoint joinPoint) System.out.println("切面类(before):...login...前置通知" ); } @AfterReturning("mypointcut()") public void afterReturning (JoinPoint joinPoint) System.out.println("切面类(afterReturning):...login...后置通知" ); } @Around("mypointcut()") public Object around (ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable System.out.println("切面类(around):...login...环绕通知-之前" ); Object obj = joinPoint.proceed(); System.out.println("切面类(around):...login...环绕通知-之后" ); return obj; } @AfterThrowing(value = "mypointcut()",throwing ="e") public void afterThrowing (JoinPoint joinPoint,Throwable e) System.out.println("切面类(afterThrowing):...login...异常通知" ); System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } @After("mypointcut()") public void after (JoinPoint joinPoint) System.out.println("切面类(after):...login...最终通知" ); } }
示例(1)-xml配置:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd " > <context:component-scan base-package ="com.*" /> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy > </aop:aspectj-autoproxy > </beans >
示例(1)-测试:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 package com.test;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import com.dao.UserDao;public class AopTest public static void main (String[] args) ApplicationContext context =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml" ); UserDao dao = (UserDao)context.getBean("userDaoImpl" ); dao.login(1 ); } }
示例(1)-无异常时的效果:
1 2 3 4 5 6 切面类(around):...login...环绕通知-之前 切面类(before):...login...前置通知 dao: ... login...1 切面类(around):...login...环绕通知-之后 切面类(after):...login...最终通知 切面类(afterReturning):...login...后置通知
示例(1)-异常时的效果:
1 2 3 4 5 6 切面类(around):...login...环绕通知-之前 Exception in thread "main" 切面类(before):...login...前置通知 切面类(after):...login...最终通知 切面类(afterThrowing):...login...异常通知 / by zero java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
4、数据库开发 4.1、使用步骤及案例 准备工作:
引入 jar 包:
commons-logging,jar
mysql-connector-java.jar
spring-beans.jar
spring-context,jar
spring-core.jar
spring-expression.jar
spring-jdbc.jar
spring-tx.jar:事务相关
spring-orm.jar:整合其他ORM框架
druid.jar:Druid连接池【可选】
XML 中配置数据源
XML 开启组件扫描
XML 配置JdbcTemplate
给每个类配置注解(@Component、@Repository、@Service、@Controller)
常见操作-见链接: JDBC-笔记 | Cyw的笔记栈
执行:jdbcTemplate.execute(String sql)
修改(增删改):jdbcTemplate.update(String sql,Object[] sql_args)
查询【返回单个Integer】:jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(String sql,Integer.class)
查询【返回对象】:jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(String sql,BeanPropertyRowMapper mapper,Object[] sql_args)
查询【返回集合】:jdbcTemplate.queryForList(String sql,BeanPropertyRowMapper mapper,Object[] sql_args)
查询【返回集合】:jdbcTemplate.query(String sql,BeanPropertyRowMapper mapper)
小结:
JdbcTemplate 的查询功能只能返回对象和列表 ,因此,当需要返回基本类型时,可以传入包装类 的字节码
JdbcTemplate 的批量操作:以batch开头的方法
数据源(无连接池版):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd " > // 数据源 <bean id ="dataSource" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource" > <property name ="driverClassName" value ="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name ="url" value ="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/springstudy" /> <property name ="username" value ="root" /> <property name ="password" value ="root" /> </bean > // jdbc模板类 <bean id ="jdbcTemplate" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" > <property name ="dataSource" ref ="dataSource" /> </bean > // 开启组件扫描(注解形式在实体类上修饰后,可以创建实体类) <context:component-scan base-package ="com.*" /> </beans >
数据源(连接池版):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd " > <bean id ="dataSource" class ="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" destroy-method ="close" > <property name ="driverClassName" value ="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name ="url" value ="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/springstudy" /> <property name ="username" value ="root" /> <property name ="password" value ="root" /> </bean > <bean id ="jdbcTemplate" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" > <property name ="dataSource" ref ="dataSource" /> </bean > <context:component-scan base-package ="com.*" /> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy > </aop:aspectj-autoproxy > </beans >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 <!--配置数据源--> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"> <!--高版本的Driver可以自动识别数据库 而不再需要指定具体是哪一个Driver了--> <property name="driverClassName" value="${druid.driverClassName}"/> <property name="url" value="${druid.url}"/> <property name="username" value="${druid.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${druid.password}"/> <!-- 初始化连接数量 --> <property name="initialSize" value="${druid.initialSize}" /> <!-- 最小空闲连接数 --> <property name="minIdle" value="${druid.minIdle}" /> <!-- 最大并发连接数 --> <property name="maxActive" value="${druid.maxActive}" /> <!-- 配置获取连接等待超时的时间 --> <property name="maxWait" value="${druid.maxWait}" /> <!--以下暂时可以不需要配置--> <!-- 配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒 --> <property name="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" value="${druid.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis}" /> <!-- 配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒 --> <property name="minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value="${druid.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis}" /> <property name="validationQuery" value="${druid.validationQuery}" /> <property name="testWhileIdle" value="${druid.testWhileIdle}" /> <property name="testOnBorrow" value="${druid.testOnBorrow}" /> <property name="testOnReturn" value="${druid.testOnReturn}" /> <!-- 打开PSCache,并且指定每个连接上PSCache的大小 如果用Oracle,则把poolPreparedStatements配置为true,mysql可以配置为false。 --> <property name="poolPreparedStatements" value="${druid.poolPreparedStatements}" /> <property name="maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize" value ="${druid.maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize}" /> <!-- 配置监控统计拦截的filters --> <property name="filters" value="${druid.filters}" /> </bean>
druid在Spring全局配置中的设置:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 <bean id ="dataSource" class ="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" > <property name ="driverClassName" value ="${druid.driverClassName}" /> <property name ="url" value ="${druid.url}" /> <property name ="username" value ="${druid.username}" /> <property name ="password" value ="${druid.password}" /> <property name ="initialSize" value ="${druid.initialSize}" /> <property name ="minIdle" value ="${druid.minIdle}" /> <property name ="maxActive" value ="${druid.maxActive}" /> <property name ="maxWait" value ="${druid.maxWait}" /> <property name ="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" value ="${druid.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis}" /> <property name ="minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value ="${druid.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis}" /> <property name ="validationQuery" value ="${druid.validationQuery}" /> <property name ="testWhileIdle" value ="${druid.testWhileIdle}" /> <property name ="testOnBorrow" value ="${druid.testOnBorrow}" /> <property name ="testOnReturn" value ="${druid.testOnReturn}" /> <property name ="poolPreparedStatements" value ="${druid.poolPreparedStatements}" /> <property name ="maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize" value ="${druid.maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize}" /> <property name ="filters" value ="${druid.filters}" /> </bean >
druid-conf.properties:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 druid.driverClassName =com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver druid.url =jdbc:mysql://217.0.0.1/springstudy?useSSL=false&characterEnding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai druid.username =root druid.password =123 druid.initialSize =10 druid.minIdle =6 druid.maxActive =50 druid.maxWait =60000 druid.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis =60000 druid.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis =300000 druid.validationQuery =SELECT 'x' druid.testWhileIdle =true druid.testOnBorrow =false druid.testOnReturn =false druid.poolPreparedStatements =false druid.maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize =20 druid.filters =wall,stat
执行语句(没有结果):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 package com.test;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import com.dao.UserDao;import com.entity.User;public class AopTest public static void main (String[] args) ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml" ); JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = (JdbcTemplate)context.getBean("jdbcTemplate" ); jdbcTemplate.execute("create table role( rid int primary key, rname nvarchar(5)); " ); } }
数据查询-封装为对象:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 package com.test;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import com.dao.UserDao;import com.entity.User;public class AopTest public static void main (String[] args) ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml" ); JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = (JdbcTemplate)context.getBean("jdbcTemplate" ); String sql = "select * from `user` where uid=1" ; BeanPropertyRowMapper<User> rowmap = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class); User user = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql,rowmap); System.out.println(user); } }
4.2、报错及解决方法 在Spring 使用外部的properties配置文件时,可能出现的问题如下:
1. MySQL拒绝本机访问-原因如下:
因为Spring在引入properties配置文件后,在使用 properties 配置文件的 username属性来配置数据源时,用了${username},但Spring本身可以使用${username}来取当前操作系统的用户名。因此,操作系统的 username与 properties 配置文件中的 username 产生冲突,并且Spring默认优先使用了操作系统的 username 去连接MySQL,而 MySQL 内此时并没有配置该username的用户,所以,拒绝本机访问
2、Maven使用Junit 测试时,报错:target\surefire-reports for the individual test results:
解决:在 pom.xml 的project内:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 <build > <plugins > <plugin > <groupId > org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId > <artifactId > maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId > <configuration > <testFailureIgnore > true</testFailureIgnore > </configuration > </plugin > </plugins > </build >
3、AOP错误error creating bean with name ‘org.springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator’:
原因:忘记导入aspectj的jar包
5、事务管理 5.1、事务的概念 事务,是数据库操作的基本单元,要么不做,要么全做。
事务的四大特性 :
原子性:一组要么不做,要么全做的操作。
一致性:从一个一致的状态 到 另一个一致的状态。
隔离性:多个事务同时执行时,各自独立,互不影响。
持久性:一旦提交,永久存储。
经典的事务应用场景:银行转账
A 转账 100 元 给 B
A少100,B多100
5.2、事务操作环境的搭建
创建数据库和数据表
定义dao层、service层的方法
JdbcTemplate注入DataSource,dao层注入JdbcTemplate,service层注入dao
事务操作的流程:
开启事务
执行操作
没有异常,提交事务
有异常,回滚事务
5.3、Spring的事务管理 事务管理 可以在任何一次添加,但一般添加到Service层 。
Spring的两种事务管理操作:
编程式:直接在代码里写
声明式:在配置文件里写,底层使用AOP
基于注解的声明式事务管理【常用】:注解+xml 或 完全注解
基于XML配置文件的声明式事务管理
Spring的事务管理的接口【事务管理器API】:
PlatformTransactionManager
DataSourceTransactionManager【供Mybatis框架使用】
5.4、注解的声明式事务管理 步骤:
在XML配置文件中,配置DataSouce 和 DataSourceTransactionManager
XML中引入·命名空间和与约束( xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"和http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.3.xsd)
开启注解声明式事务 ,<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" />
在Service层的类或方法 上添加事务注解 :@Transactional
【使用时,删除以下配置的注释】
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.3.xsd " > <context:component-scan base-package ="com.*" > </context:component-scan > <aop:aspectj-autoproxy /> // 数据源 // <context:property-placeholder location ="classpath:d.properties" /> <bean id ="dataSource" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource" > <property name ="driverClassName" value ="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name ="url" value ="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/springstudy" /> <property name ="username" value ="root" /> <property name ="password" value ="root" /> </bean > // jdbc模板类 <bean id ="jdbcTemplate" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" > <property name ="dataSource" ref ="dataSource" /> </bean > // 事务管理 <bean id ="transactionManager" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" > <property name ="dataSource" ref ="dataSource" /> </bean > // 开启注解声明式事务管理 <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager ="transactionManager" /> </beans >
@Transactional 注解事务管理的参数的配置:
propagation:事务的传播行为【见下表】。管理多个事务方法的调用过程。
isolation:事务的隔离级别。为解决【污读、不可重读、幻读】
timeout:超时时间。规定时间内提交,不提交就回滚(默认值 = -1秒 )
reayOnly:是否只读。默认值为false
rollbackFor:回滚。设置发生哪些异常的时候,回滚数据。
noRollbackFor:不回滚。设置发生哪些异常的时候,不回滚数据。
事务的传播行为:
传播属性
描述
REQUIRED (即:Required)
若已有事务在运行,则当前方法就在该方法内运行;否则新建一个事务再运行该方法。
REQUIRED_NEW (即:Required_new)
若已有事务在运行,则挂起该事务,并创建一个新事务来运行该方法
SUPPORTS(即:Supports)
有事务,则运行在该事务;无事务,则可以直接运行
NO_SUPPORTED(即:No_Supported)
不可运行在事务;有事务,则先挂起事务
MANDATORY(即:Mandatory)
必须运行在事务中;无事务,则报异常
NEVER(即:Never)
不可运行在事务中;有事务,则报异常
NESTED(即:Nested)
有事务,在该事务的内部事务中运行;无事务,则新建事务,在新事务内运行
事务的传播行为的使用:
1 2 3 4 5 @Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED) @Service class UserService }
事务的读的问题:
涉及事务的隔离性。有三个读的问题
污读:一个未提交的事务 读到 另一个未提交的事务的数据
不可重读:一个未提交的事务 读到 一个已提交的事务 修改的数据
幻读:一个未提交的事务 读到 一个已提交的事务 添加的数据
解决事务的读的问题:
设置事务的隔离级别:
读未提交(read uncommited):没解决
读已提交(read commited):解决 脏读
可重复读(repeated_read):解决 脏读、不可重读【MySQL默认 的隔离级别】
序列化(serializable):解决 脏读、不可重读、幻读
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED, isolation=Isolation.REPITEDABLE_READ) @Service class UserService }
5.5、XML的声明式事务管理 步骤:
XML中配置事务管理器
配置 切面类的“通知”方法
配置 切面类、切点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.3.xsd " > // 数据源 <bean id ="dataSource" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource" > <property name ="driverClassName" value ="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name ="url" value ="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/springstudy" /> <property name ="username" value ="root" /> <property name ="password" value ="root" /> </bean > // jdbc模板类 <bean id ="jdbcTemplate" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" > <property name ="dataSource" ref ="dataSource" /> </bean > // 事务管理 <bean id ="transactionManager" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" > <prpperty name ="dataSource" ref ="dataSource" /> </bean > // --------------------------------------------------- // 配置通知 <tx:advice id ="txAdvice" > // 配置事务参数 <tx:attributes > // 在哪个方法上添加事务【2种方式】 <tx:method name ="addMoney" propagation ="REQUIRED" /> <tx:method name ="add*" propagation ="REQUIRED" /> </tx:attributes > </tx:advice > // 配置切点和切面 <aop:config > <aop:pointcut id ="pt1" expression ="execution(* com.service.UserService.addMoney(..))" /> <aop:advisor advice-ref ="txAdvice" pointcut-ref ="pt1" /> </aop:config > </beans >
6、Spring5 新功能介绍 介绍:
Spring 5 是基于JDK 8兼容JDK 9的,剔除了以往不建议使用的类和方法。
Spring 5 自带通用的日志框架封装【官方建议使用:Log4j2】
Spring 5 @Nullable注解,可以作用在方法(返回值为空)、属性、参数(值可以为空)
Spring 5 支持函数式编程【lambda表达式】:用户手动new的对象交给Spring来管理
Spring 5 整合 Junit5【指定Junit版本:@RunWith(SpringJunit4ClassRunner.class); 指定配置文件的路径:@ContextConfiguration(lasspath:bean1.xml)】
7、WebFlux 7.1、WebFlux简介 【建议此模块学习前,先学SpringBoot】
7.2、WebFlux的执行流程与核心API 7.3、WebFlux-基于注解的编程模型 7.4、WebFlux-基于函数式的编程模型